In other words, it measures how much money each additional sale “contributes” to the company’s total profits. Where C is the contribution margin, R is the total revenue, and V represents variable costs. The contribution margin can be stated on a gross or per-unit basis. It represents the incremental money generated for each product/unit sold after deducting the variable portion of the firm’s costs. The variable costs equal $6 because the company pays $4 to manufacture each unit and $2 for the labor to create the unit.
How is contribution margin calculated?
That is it does not include any deductions like sales return and allowances. Thus, the total variable cost of producing 1 packet of whole wheat bread is as follows. Investors and analysts use the contribution margin to evaluate how efficient the company is at making profits. For example, analysts can calculate the margin per unit sold and use forecast estimates for the upcoming year to calculate the forecasted profit of the company.
Total Cost
The contribution margin (CM) is the profit generated once variable costs have been deducted from revenue. Investors and analysts may also attempt to calculate the contribution margin olive and poppy 1 figure for a company’s blockbuster products. For instance, a beverage company may have 15 different products but the bulk of its profits may come from one specific beverage.
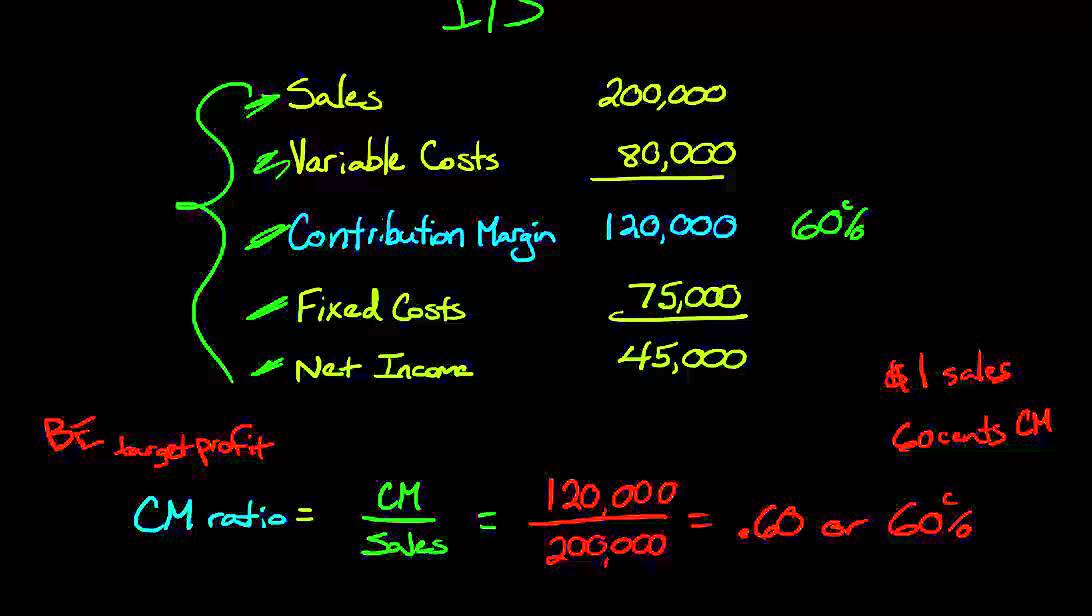
- The CM ratio can be interpreted as the percentage of each sale that is left over after variable costs are covered, to contribute towards fixed costs and profits.
- For example, if the cost of raw materials for your business suddenly becomes pricey, then your input price will vary, and this modified input price will count as a variable cost.
- The CM ratio is a useful tool for managers when making decisions such as setting sales prices, selecting product lines, and managing costs.
- In the dynamic world of business, understanding key financial indicators is essential for effective decision-making.
- After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career.
What is your current financial priority?
If the total contribution margin earned in a period exceeds the fixed costs for that period, the business will make a profit. If the total contribution margin is less than the fixed costs, the business will show a loss. In this way, contribution margin becomes an important factor when calculating your break-even point, which is the point at which sales revenue and costs are exactly even ($0 profit). This, in turn, can help you make better informed pricing decisions, but break-even analysis won’t show how much you need to cover costs and make a profit.

Contribution Margin: Definition, How to Calculate & Examples
In these examples, the contribution margin per unit was calculated in dollars per unit, but another way to calculate contribution margin is as a ratio (percentage). The difference between fixed and variable costs has to do with their correlation to the production levels of a company. As we said earlier, variable costs have a direct relationship with production levels.
Is contribution margin the same as profit?
It provides one way to show the profit potential of a particular product offered by a company and shows the portion of sales that helps to cover the company’s fixed costs. Any remaining revenue left after covering fixed costs is the profit generated. The contribution margin ratio of a business is the total revenue of the business minus the variable costs, divided by the revenue. Contribution margin is the remaining earnings that have not been taken up by variable costs and that can be used to cover fixed costs. Profit is any money left over after all variable and fixed costs have been settled. For every additional widget sold, 60% of the selling price is available for use to pay fixed costs.
This is one of several metrics that companies and investors use to make data-driven decisions about their business. As with other figures, it is important to consider contribution margins in relation to other metrics rather than in isolation. A key characteristic of the contribution margin is that it remains fixed on a per unit basis irrespective of the number of units manufactured or sold. On the other hand, the net profit per unit may increase/decrease non-linearly with the number of units sold as it includes the fixed costs.
To make a new cup, you have to spend $2 for the raw materials, like ceramics, and electricity to power the machine and labor to make each product. The higher a product’s contribution margin and contribution margin ratio, the more it adds to its overall profit. In the same case, if you sell 100 units of the product, then contributing margin on total revenue is $6,000 ($10,000-$4,000). Further, it is impossible for you to determine the number of units that you must sell to cover all your costs or generate profit. Thus, it will help you to evaluate your past performance and forecast your future profitability. Accordingly, you need to fill in the actual units of goods sold for a particular period in the past.

